Continuous Casting Simulation
The specialized module allows for setting any geometry of the crystallizer and the trajectory of the ingot's movement in the installation, taking into account the thermal and force interaction with all the elements of the traction, guide mechanisms, etc.
- Temperature and phase fields
- Slab solidification
- Macro and microporosity
- Residual stresses
- Cracks (hot and cold)
- Elastic deformations
- Plastic deformations
- Metal structure
PoligonSoft enables investigation into the influence of various technological parameters on the quality of the parts, identifying the relationship between variations of these parameters and the occurrence of defective parts.
Cost and Time Reduction
Save significant costs in materials and labor, in addition to reducing product development time.
Improve Quality and Precision
Prevent and correct casting defects, such as porosity, air inclusions, or solidification issues.
Process and Design Optimization
Experiment with different variables of the casting process to find the most efficient configuration.
General Concept
The mathematical model was developed in collaboration with a large producer of steel sheets and plates, Severstal company. It is based on the Fourier thermal solver and the Hooke stress solver, for which a new and unique solution scheme was designed.

In creating the continuous casting model, we took into account both the advantages and the disadvantages of other approaches to addressing this problem. As a result, our solution allows for more complete modeling of the continuous casting process in comparison with similar solutions.
What we offer:
- Modeling of the continuous casting process of products of any section (rectangular, circular, etc.).
- Ability to define any trajectory of slab movement.
- User-friendly and easy-to-handle interface.
- Capability to calculate stresses.
Semi-Continuous Casting Analysis
Study conducted for OJSC "KUMZ"
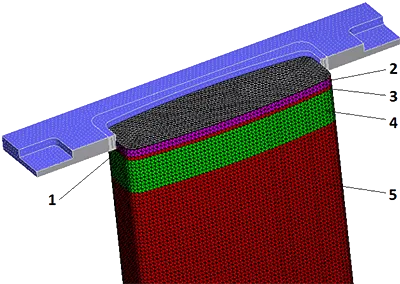
- 1- Metal Level in the Crystallizer
- 2- Thermal Interaction Zone with the Crystallizer
- 3- Space Before the Cooling Zone
- 5- Water Cooling Zone
- 6- Area Below the Level of the Drains
An analysis is required for typical casting regimes, to find the temperature distribution in the established regime, predict the integrity of the ingot, and examine the characteristics of the residual stresses.
- Alloy: D19ch brand aluminum alloy
- Ingot Section: 1671x492, barrel shape, height 6700 mm
- Crystallizer Height: 115 mm
- Metal Temperature (in the mixer): 710 °C
- Crystallizer: 6061-T6 brand aluminum alloy
- Cooling Water Temperature: 25 °C
- Ambient Temperature: 20 °C
- Metal Level in the Crystallizer: 55 mm from the top
- Water Cooling Zones: 30 mm below the lower edge of the crystallizer, extending 270 mm
- The cooling zones are bounded at the bottom by drainage systems that completely remove the water below their level.
Thermal Calculation Results with a Casting Speed of 50 mm/min

Animation: temperature and phase fields during the ingot solidification (longitudinal section along the wide face)
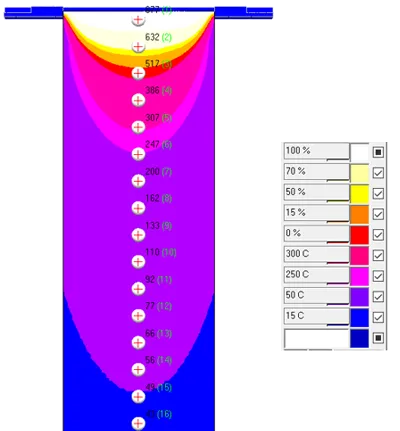
Temperature distribution along the ingot (step of 300 mm, cross-section) in steady state regime.
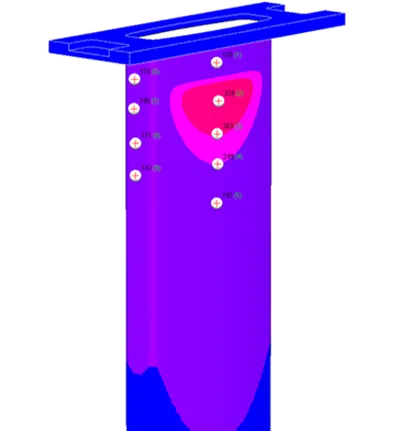
Secondary reheating of the ingot surface below the level of the drains (steady state regime).
Characteristics of Steady State Regime (50 mm/min)
Reaching a steady thermal regime in casting means the stabilization of the characteristics of the structure and properties of the metal throughout the volume of the ingot. The most significant factor in this case is the stabilization of temperatures and dimensions of the liquid metal cavity.
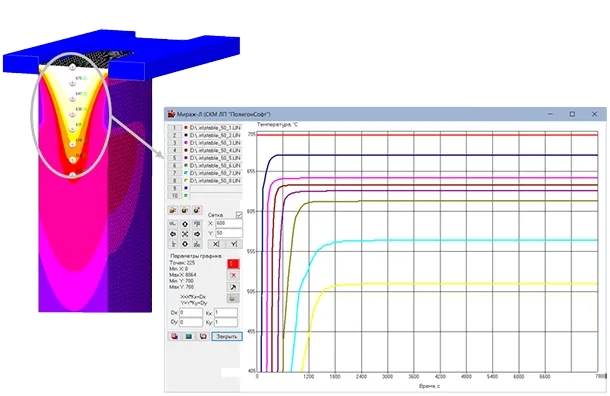
Increase in temperatures as the ingot passes through the control points (1-8 in the longitudinal cut along the narrow edge; interval of marking points of 100 mm, counting from the level in the crystallizer) and their stabilization over time during the casting cycle period.
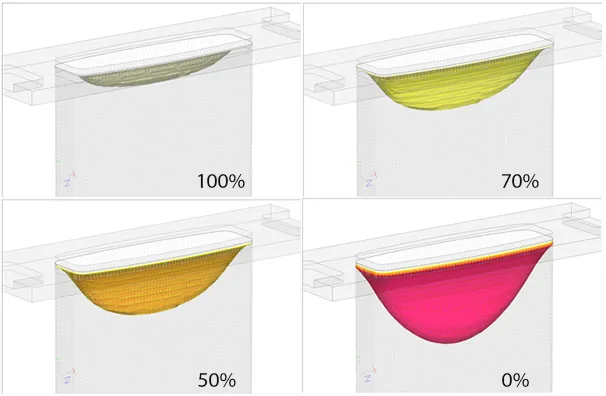
Position of the liquid phase isosurfaces within the volume of the cavity.
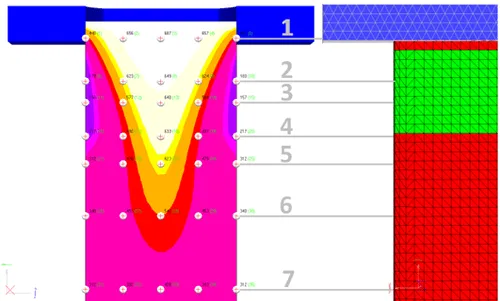
Control levels, with temperature distributions along the thickness of the ingot in relation to cooling zones on the surface (in green on the right)
Stress-Strain State Analysis
Reaching a steady thermal regime in casting means the stabilization of the characteristics of the structure and properties of the metal throughout the volume of the ingot. The most significant factor in this case is the stabilization of temperatures and dimensions of the liquid metal cavity.
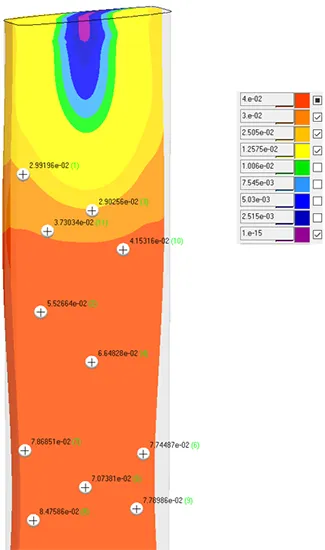
Displacement Field (x20)
Intensity of Plastic Deformations
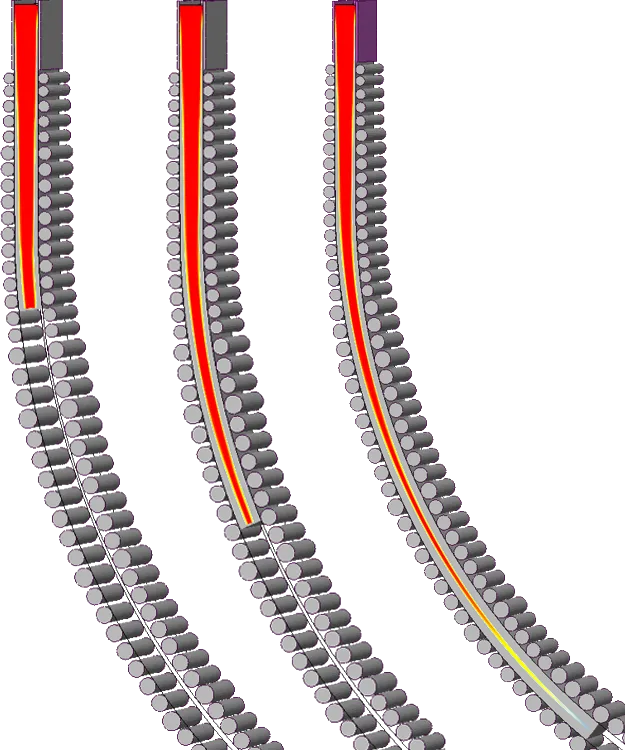
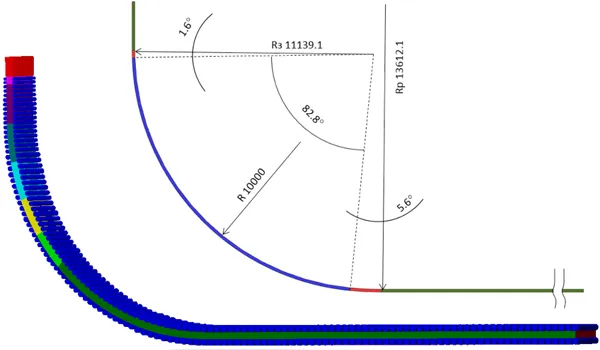
Continuous Casting Analysis
A study conducted for the company "Severstal" aimed to compare the results obtained in simulation with the actual results of their casting machine.
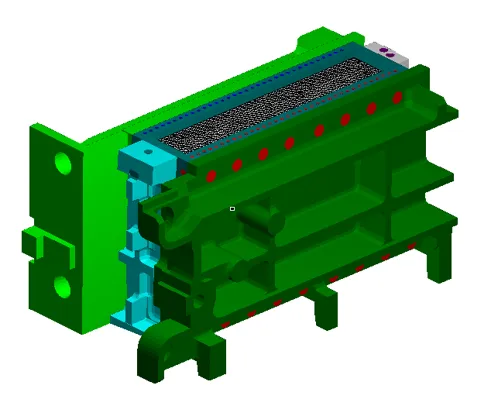
3D Model of the Continuous Steel Casting Installation No. 2 of PAO 'Severstal'. The secondary cooling zones are shown in color.
3D Model of the Crystallizer

Cooling Channels within the Crystallizer
Filling (speed)

Since PoligonSoft can simulate flow processes, it's possible to model how, at the beginning of the process, the mold is filled with molten metal from the ladle and then use these temperatures for subsequent calculations.
Filling (temperature distribution)

An accurate model of the crystallizer is used to study how the casting speed affects the thickness of the solid layer that forms on the slab.
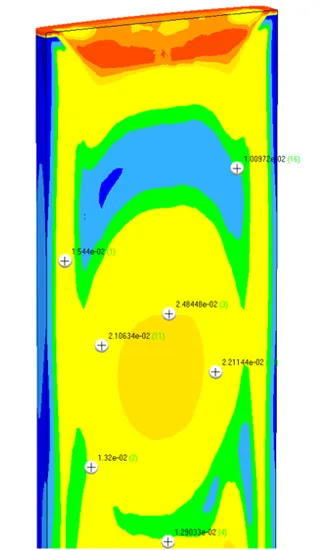
Temperature Verification
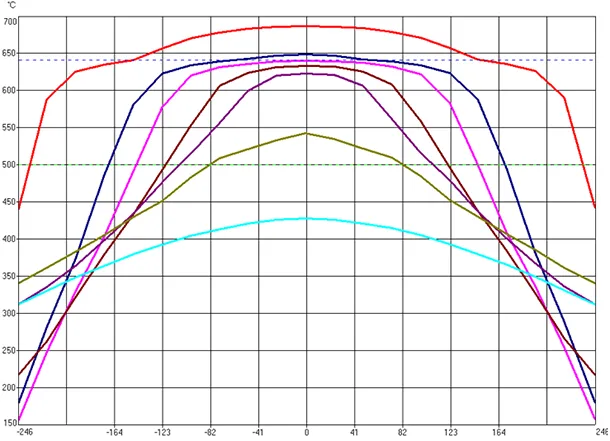
Comparison of the temperature at control points obtained as a result of the simulation with the actual temperatures on the thermocouples of the casting machine considering water cooling.

Simulation of the Stress-Strain State
We use an elastoplastic model that allows modeling of elastic and plastic deformations and an additional criterion to evaluate the probability of cold crack formation on the surface of the slab.



