Heat Treatment
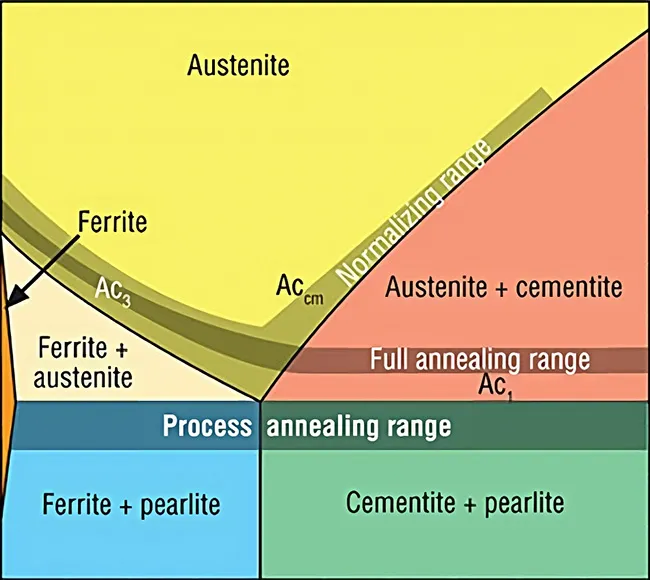
The specialized module allows for the prediction of the structure and mechanical properties of structural and low-alloy steels after undergoing heat treatment: quenching, normalizing, or annealing.
- Temperature and phase fields
- Slab solidification
- Macro and microporosity
- Residual stresses
- Cracks (hot and cold)
- Elastic deformations
- Plastic deformations
- Metal structure
Cost and Time Reduction
Save significant costs in materials and labor, in addition to reducing product development time.
Improve Quality and Precision
Prevent and correct casting defects, such as porosity, air inclusions, or solidification issues.
Process and Design Optimization
Experiment with different variables of the casting process to find the most efficient configuration.
Heat Treatment Model
The model enables the prediction of metal characteristics following heat treatment.
Input Parameters:
Fourier Solver:
Heat Treatment Module:
Simulation of:
- Quenching
- Normalizing
- Annealing
- Tempering
Results:
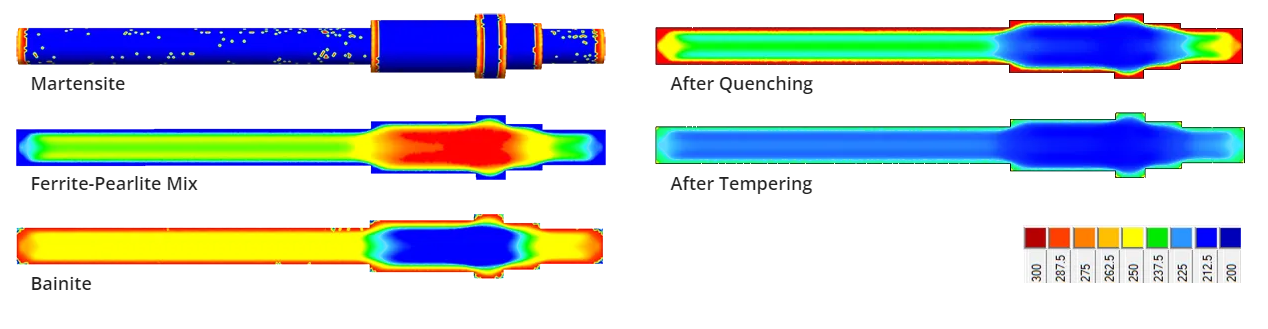
- Structure (martensite, bainite, ferrite-pearlite mix)
- Vickers Hardness
- Yield Strength
- Tensile Strength
- Relative Elongation
Heat Treatment of 40Х Steel Shaft
A study conducted to understand the causes of the fracture of a shaft after heat treatment performed by the producer.
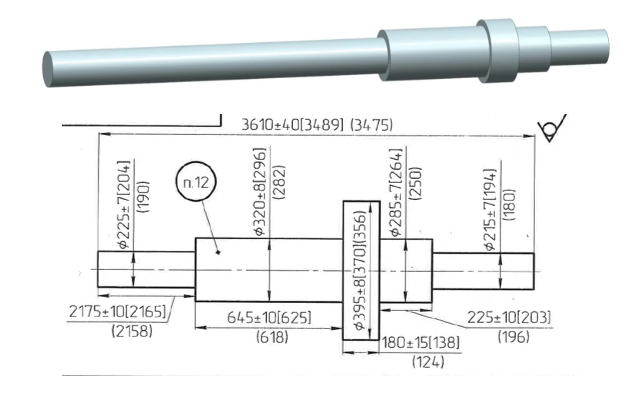
- Oil Quenching
- Initial Temperature of the Shaft: 1000 °C
- Heat Transfer to Oil: 1500 W/(m²K)
- Retention Time: until the surface temperature reaches 200 °C
- Air Cooling: Down to 20 °C
- Heat Transfer to Air: 10 W/(m²K)
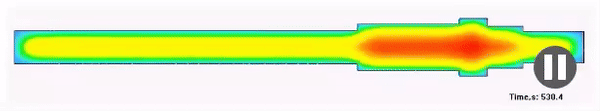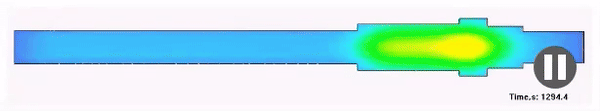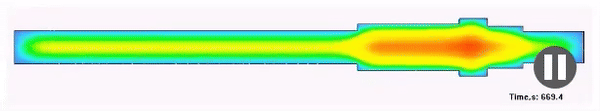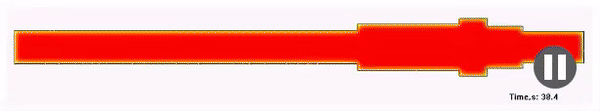
Structure
Result of the calculation of the metal structure after quenching
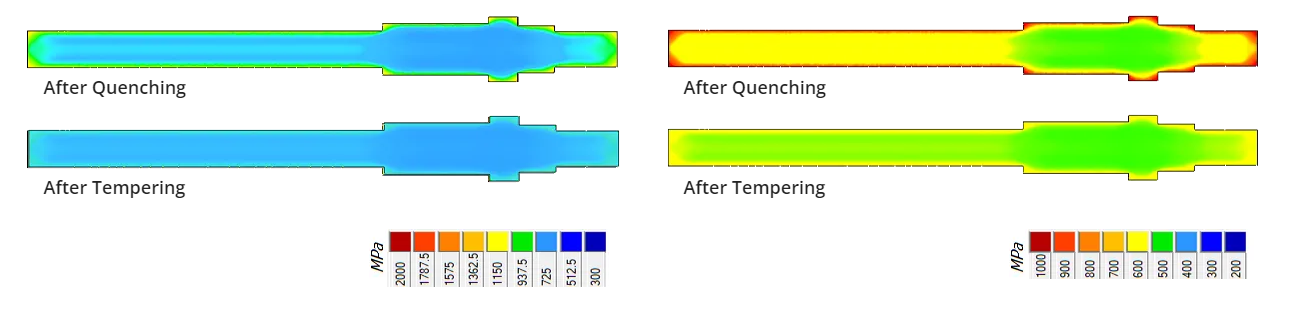
Vickers Hardness
Result of the calculation of Vickers hardness after quenching and tempering
Tensile Strength
Result of the calculation of tensile strength
Yield Strength
Result of the calculation of yield strength after quenching and tempering